https://www.plt.org/educator-tips/videos-climate-change-middle-school
Climate change. Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=154&v=ztWHqUFJRTs&feature=emb_logo
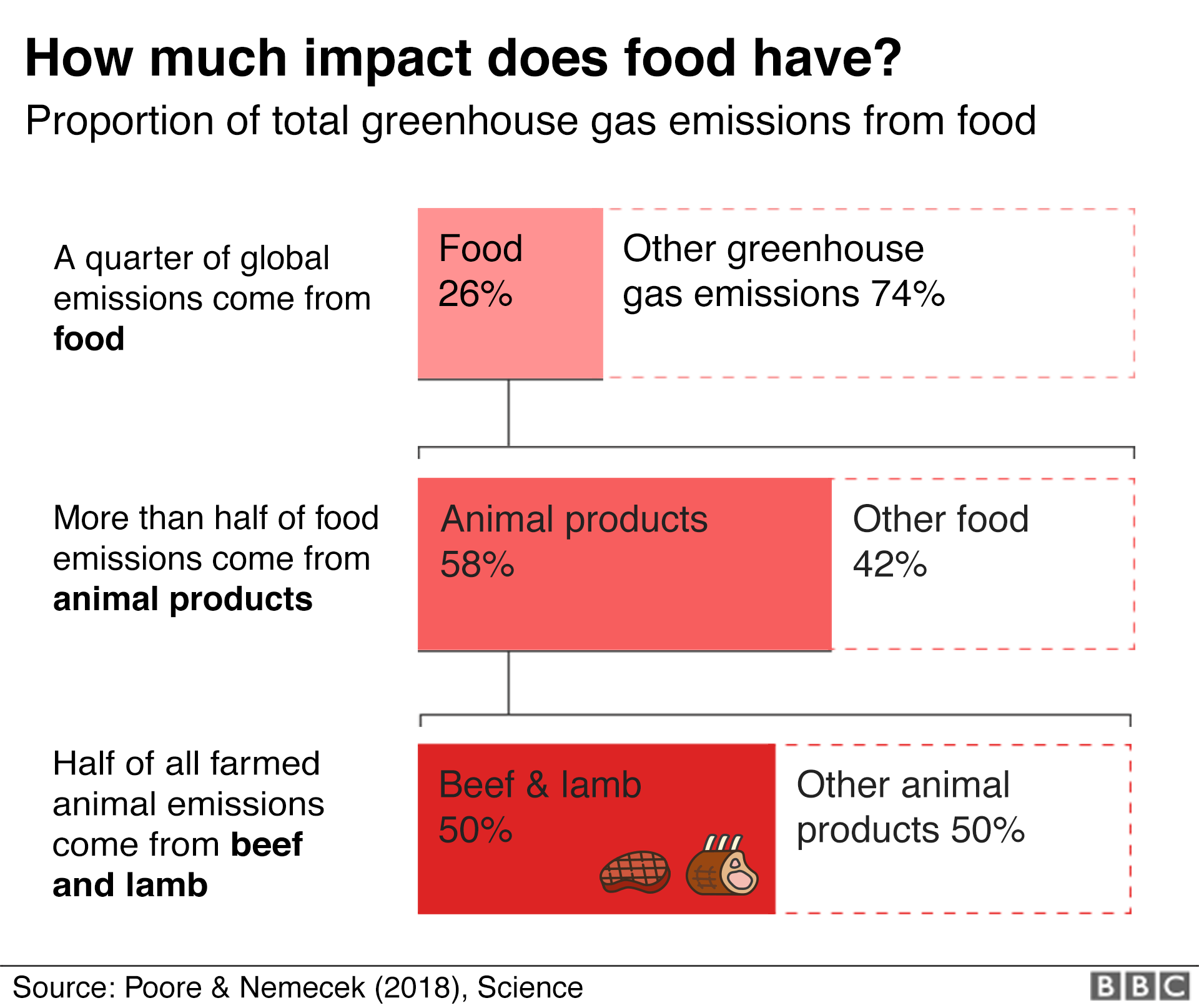
Climate change food calculator: What's your diet's carbon footprint?
How do your food choices impact on the environment?
says we need to buy less meat, milk, cheese and butter - but also eat more locally sourced seasonal food, and throw less of it away.
Compost Food Waste
Today, an estimated one-third of all the food produced in the world goes to waste.
But wasted food isn't just a social or humanitarian concern—it's an environmental one. When we waste food, we also waste all the energy and water it takes to grow, harvest, transport, and package it. And if food goes to the landfill and rots, it produces methane—a greenhouse gas even more potent than carbon dioxide. About 11% of all the greenhouse gas emissions that come from the food system could be reduced if we stop wasting food.
How you throw your food away also matters. Organic matter rotting in a landfill releases methane, a greenhouse gas several times more potent than carbon dioxide. But if you compost your leftovers in a well-maintained bin that lets in oxygen, you’ll significantly reduce the amount of methane released into the atmosphere and the carbon in the composting organic matter will be held in the resulting soil.
Composting reduces greenhouse gas emissions and returns vital nutrients to the soil, and we can all make a difference. Is it time to invite composting into your life?
If you don’t have space for a compost bin, you can get together with members of your local community to compost together
BUY LOCAL, SEASONAL, ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY FOOD
Food grown close to home helps prevent global warming because it requires less fossil fuels to transport, generating fewer GHG emissiones than conventionally produced food.
Seasonal food requires less energy to grow and transport. It has a smaller footprint.
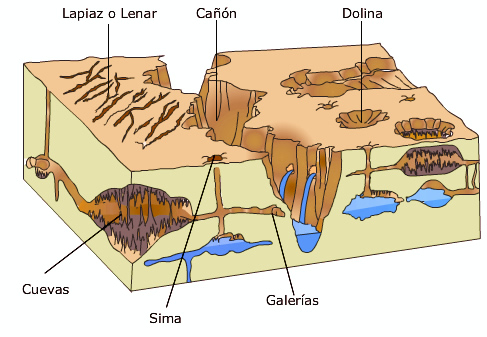
Modelado karstico de mihayedo
Acuífero libre: aquellos en los que el nivel del agua, al perforarlos con un pozo o sondeo, queda a a misma altura en que se cortó. El límite superior de la zona saturada de agua (véase nivel freático) se encuentra a presión atmosférica.
Acuíferos cautivos, artesianos o confinados: los que están tapados a presión por una capa impermeable situada encima. El acuífero se encuentra completamente saturado y la presión a la que se encuentra sometida el agua es superior a la atmosférica.
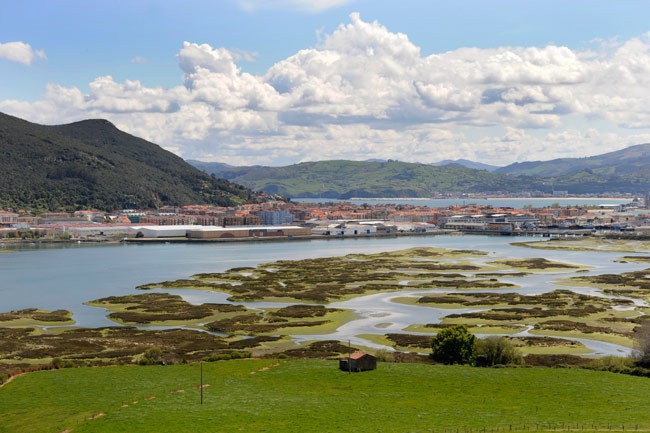
Bahía. Ejemplo la bahía de Santander
Es una entrada de un mar, océano o lago rodeada por tierra excepto por una apertura
Estuario. Ejemplo estuario del río Miño
Es la desembocadura, en el mar, de un río amplio y profundo e intercambia en esta agua salada y agua dulce, debido a las mareas. La desembocadura del estuario está formada por un solo brazo ancho en forma de embudo ensanchado.
Marisma. Ejemplo marismas de santoña
Terreno pantanoso situado por debajo del nivel del mar, que ha sido invadido por las aguas del mar o de una ría.
Vídeo sobre el fracking
Animación fracking




















No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario