Enlace libro digital anaya
UNIT 1- THE PLANT KINGDOM
Picture showing types of leaves
App identify tree leaves
Homework-Quizizz
Tuesday 29th of September 2020
- Review online activity flowering- non-flowering plants
Review online activity type of leaves
- Review online activity, parts of a plant
- Review activity. What part of the plant do you eat when...?
Look at this picture. Are there any differences between these two trees?
Evergreen/Deciduous/Marcescent trees
Why do leaves change color in autumn?
Thursday 1st of October 2020
Marcescent leaves
The leaves remain during autumn and winter until the new leaves come up. Mainly in young trees. The leaves become brown but they don´t fall.
Examples: oak tree, beech tree
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
CO2 + H2O + light energy → O2 + organic matter + chemical energy
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2
The organic matter contains carbon. Plants get carbon from carbon dioxide.
Video photosynthesis
Photosynthesis song
Review online activity photosynthesis
Next lesson
Interaction with the environment
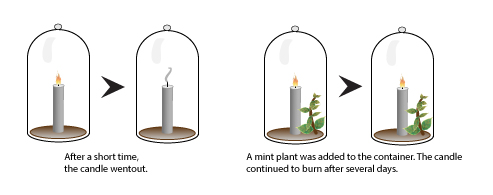
Experiment
This year most of the experiments will be done at home. I will explain all the steps and things needed to do each of them successfully!
¡¡¡¡Explaining our experiment with genially!!!
Links to experiment
Enlace en español
POWERPOINT PRESENTATION
FOLLOW-UP ACTIVITIES
Video about our solar system
Video Mercury
Video Venus
Video Mars
Video Jupiter
Video Saturn
Video Uranus
Video Neptune
Video Pluto
Video about Halley comet
Jupiter The red spot
Ciclone en el polo NOrte de Júpiter
Triple crater sobre Marte
Los anillos de Saturno
Vídeo Comparación de tamaños en el universo
What is the Sun?
How far is it from the Earth?
What do you know about the Sun? Composition? Parts?
Why do the planets go around the Sun?
Will it last forever?
Video about the SUn
The Sun creates a gravitational force that causes nearby planetary bodies to be drawn toward it


Vida y muerte de una estrella
Other celestial bodies:
What is the difference between comets, asteroids, meteoroids, meteors, and meteorites?


What are shooting stars?
Gemínidas, perséidas, acuáridas, oriónidas a qué deben su nombre?
Video Shooting stars
Vídeo ¿Qué es una lluvia de estrellas?
Why is there life on Earth?
What characteristics allow life on Earth?
Video Why is their life on Earth
Video magnetosphere (start minute 2:19)
Video magnetosphere, solar wind, and aurora borealis (iniciar en minuto 2:55)
Review activity layers of the Earth
Video The Earth
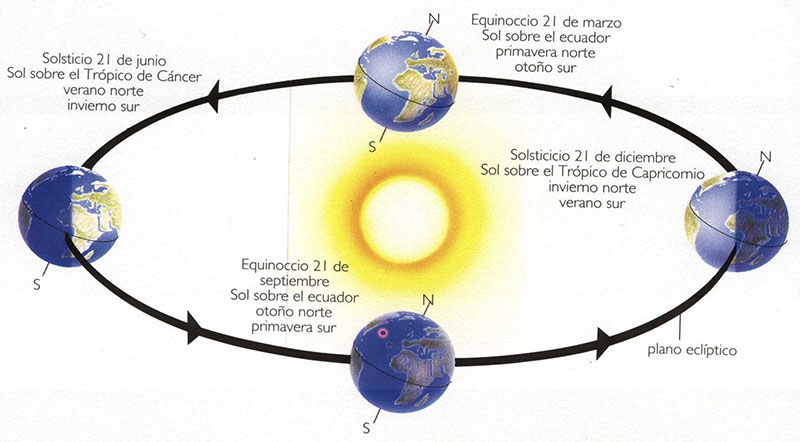
The movements of Earth
Pages 14 and 15 Book
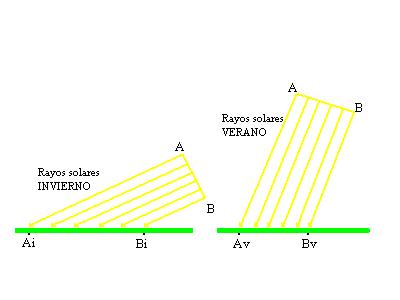
What causes the seasons?
The Earth´s axis is tilted
Rotation
The movement of revolution
In the Northern Hemisphere during:
- Summer The Earth is tilted towards the Sun.
-Winter The Earth´s axis is tilted away from the Sun.
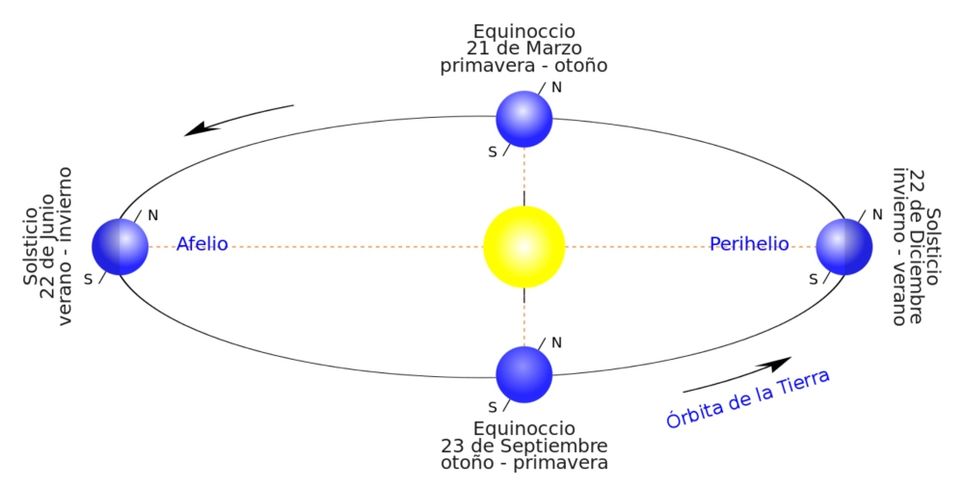
What is the equinox?
What is the winter solstice? Summer solstice?
Book Page 15 activity 7.
Book pages 16 and 17
Video The seasons/the movement of revolution
Page 20 activity 10.
Afelio y perihelio
The Moon
What is the Moon?
How was it formed?
Can we see both sides of the Moon?
What are the phases of the Moon? Can you explain each of them?
Video The Moon
- Vídeo fases de la Luna vistas desde la Tierra (desde minuto 2:10)
- Vídeo ¿Por qué vemos siempre la misma cara de la Luna?
¿Cómo see verá la Luna desde la Tierra en cada una de las posiciones de la siguiente imagen?
Eclipses
What is an eclipse?
A solar eclipse? A lunar eclipse? Make a drawing of each type
Activity
Video Solar eclipse
Video Lunar eclipse
What are the tides? What causes them?
How many tides happen in one day on Gijon´s beach?
Video las mareas
Spring tides and neap tides
Vídeo mareas muertas y vivas (sin sonido solo música)
Homework
Draw in your notebook the movements of rotation (axis, equator) and revolution: say what season is it in the northern and southern hemisphere in each of the 4 positions.
Draw a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse
Review activities
Other videos
Vídeo compara distancias y tamaños del sistema solar
Vídeo comparación tamaños
Vídeo sobre las constelaciones
Vídeo movimiento aparente estrellas
Wintertime/The time change
Video the winter solstice
Questions about the video
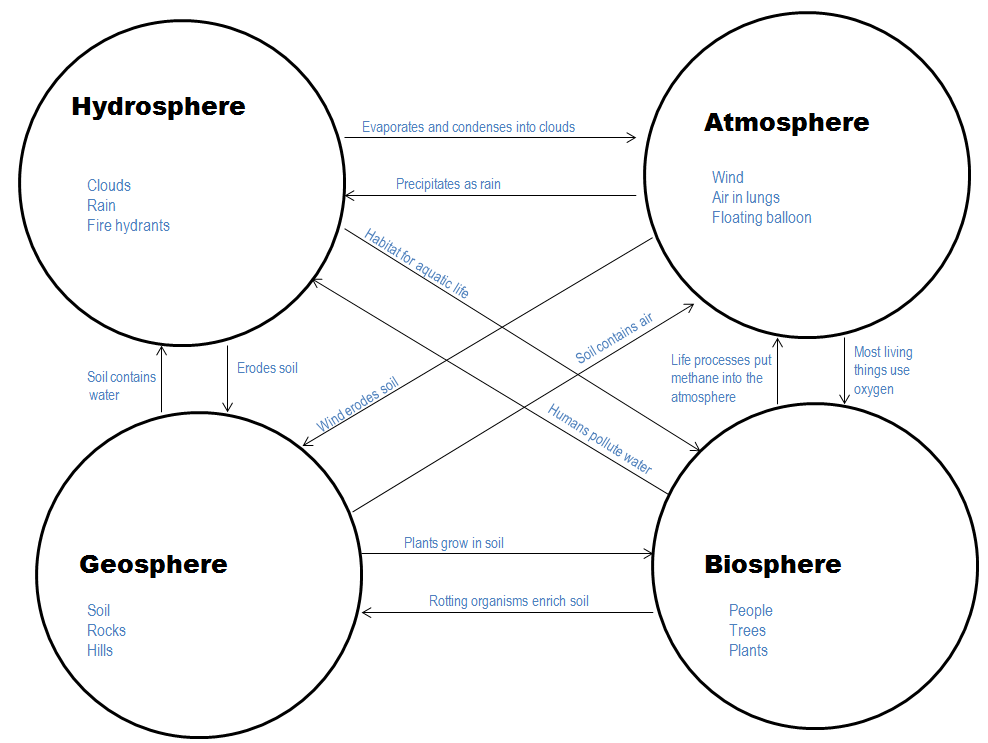
In the next units, we will study the 4 spheres of our planet. Remember they are interconnected
UNIT 4- THE GEOSPHERE
What is the geosphere?
What can we find inside the Earth?
What layers are inside the Earth?
What are the main characteristics of each layer?
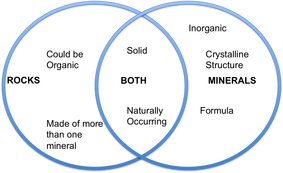
Are rocks and minerals the same thing? What differences are there?
Do you remember the main characteristics of a mineral?
Examples of properties of minerals?
What is the Mohs scale?


Minerals are the building blocks of rocks

How can we identify minerals? What properties do they have?
Hardness: The Mohs scale
"Hardness" is the resistance of a material to being scratched.
1. If Specimen A can scratch Specimen B, then Specimen A is harder than Specimen B.
2. If Specimen A does not scratch Specimen B, then Specimen B is harder than Specimen A.
3. If the two specimens are equal in hardness then they will be relatively ineffective at scratching one another. Small scratches might be produced, or it might be difficult to determine if a scratch was produced.
4. If Specimen A can be scratched by Specimen B but it cannot be scratched by Specimen C, then the hardness of Specimen A is between the hardness of Specimen B and Specimen C.
Classification of minerals according to their composition
Go to page 32-33 in your book and answer these:
- What are the two main types of minerals?
- Page 33 activity 2
- Page 33 activity 3
Game mineral identification
Game rocks classification
ROCKS
What do you know about rocks?
What are they?
How are they formed?
Examples?
Look at these pictures:
What is it? Is it connected to rocks?
How were these materials formed?
View 360º volcanic landscape
Other types of rocks, Picos de Europa
What about these?

Video about rocks
Video comprehension activity
Online activity
Page 34 Book
THE ROCK CYCLE
Video the rock cycle
Give them the photocopy, read it, they must cut it at home.
eNLACE
Amazing places in Spain related to the geosphere. ¡Hagamos geoturismo!
La geoda de Pulpi, Almería
Las cuevas de Valporquero
Volcán Cerro Gordo, Guadalajara, Campo de Calatrava
Las Médulas
Flysch Zumaia
Parque geológico costa quebrada Cantabria
Geoparque de las Loras Burgos
Las minas de riotinto Huelva
Para quien quiera ampliar información os dejo enlace a la Guía del patrimonio geológico de algunas zonas de la provincial de León
THE ATMOSPHERE
Primitive atmosphere/ actual atmosphere
Composition
Structure: layers
Functions
Air pollution problems/Pollutants
Homework: Cut out about the atmosphere
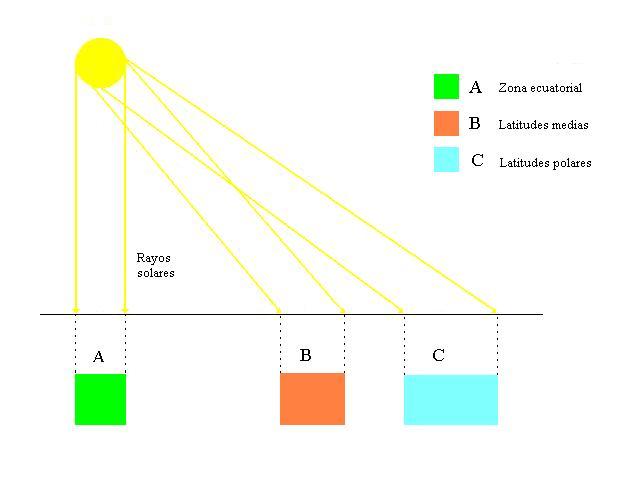
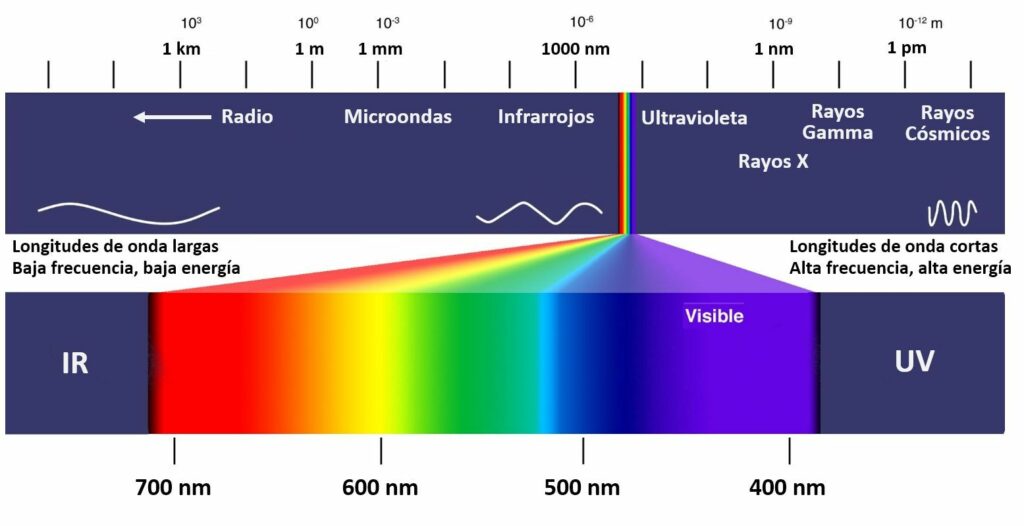
La energía solar llega en forma de radiación electromagnética o luz.
La radiación electromagnética, son ondas.
Se puede ordenar en un espectro en diferentes longitudes de onda, a menor longitud de onda mayor contenido energético.
El Sol emite energía en forma de radiación de onda corta, principalmente en la banda del ultravioleta, visible y el infrarrojo cercano
La región visible (entre 400 nm < < 700 nm) corresponde a la radiación que puede percibir la sensibilidad del ojo humano e incluye los colores: violeta (420 nm), azul (480 nm), verde (520 nm), amarillo (570 nm), naranja (600 nm) y rojo (700 nm).
La luz de color violeta es más energética que la luz de color rojo, porque tiene una longitud de onda más pequeña.
La radiación con las longitudes de onda más corta que la correspondiente a la luz de color violeta es denominada radiación ultravioleta.
La radiación proveniente del sol contiene tres tipos de rayos:
-El 50% son rayos infrarrojos (IR) que proporcionan calor.
-El 40% son rayos visibles (VI) que proporcionan luz. -
-El 10% son rayos ultravioleta (UV) que aportan a nuestro cuerpo tanto beneficios como peligros al mismo tiempo
Diagram showing how different types of UV radiation penetrate or interact with the ozone layer.
The most common form of UV radiation is sunlight, which produces three main types of UV rays:
UVA rays have the longest wavelengths, followed by UVB, and UVC rays which have the shortest wavelengths. While UVA and UVB rays are transmitted through the atmosphere, all UVC and some UVB rays are absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer.
So, most of the UV rays you come in contact with are UVA with a small amount of UVB.
Both UVA and UVB rays can cause damage to your skin.
Sunburn is a sign of short-term overexposure, while premature aging and skin cancer are side effects of prolonged UV exposure.
Video shows how sun screen protects us from UV rays
Una grabación con lentes ultravioletas revela la importancia de aplicarse protección solar y cómo afectan las radiaciones y el paso del tiempo a la piel
GREENHOUSE EFFECT
Video increase of the greenhouse effect
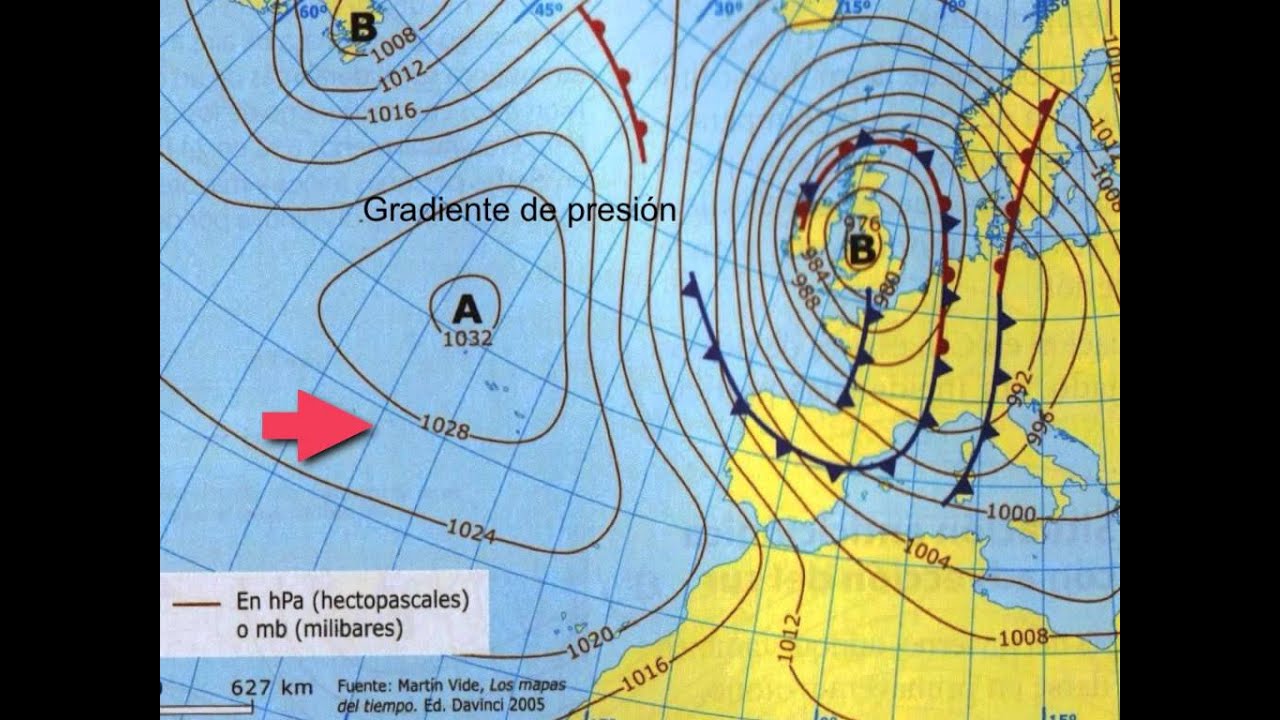
INTERPRETACIÓN DE MAPAS METEOROLÓGICOS
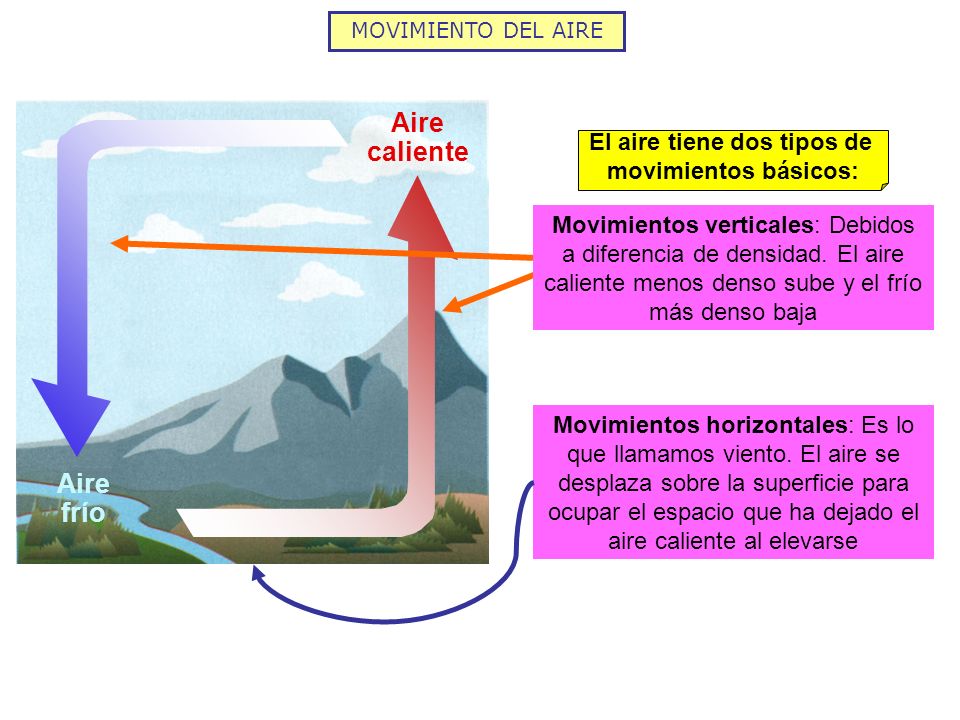
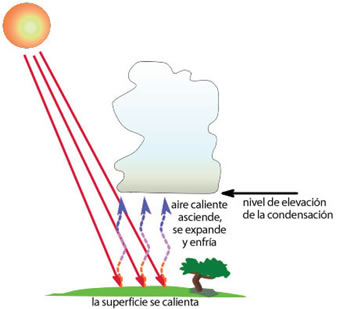
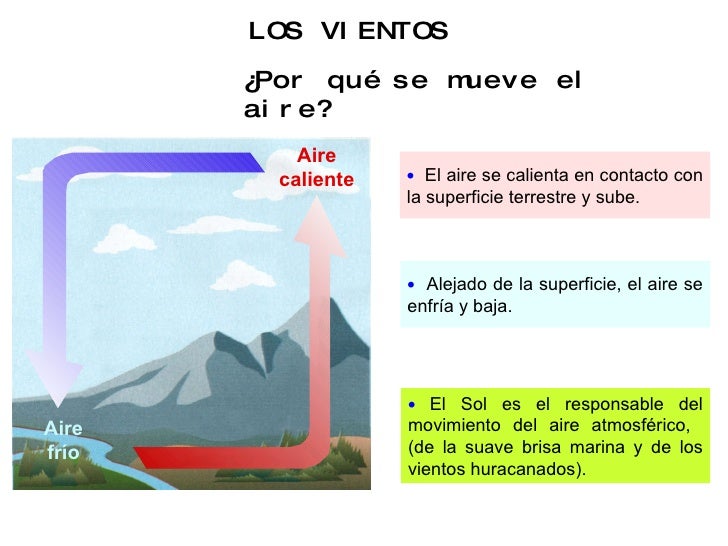
¿Qué es el viento?, ¿Cómo se calienta el aire?, ¿Aire caliente, aire frío cuál es más denso?
¿Qué son? ¿Qué información nos dan?
¿Qué son las isobaras?
¿Qué es un anticiclón?, ¿Y una borrasca?
¿Cómo se mueve el aire en cada uno en el hemisferio norte?
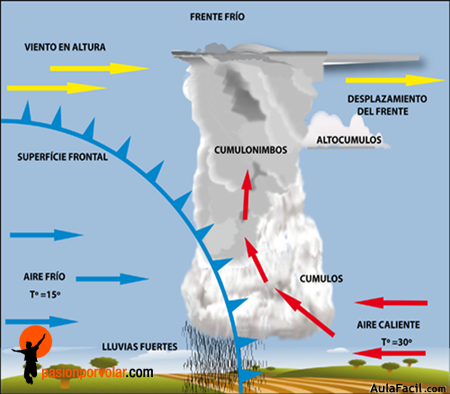
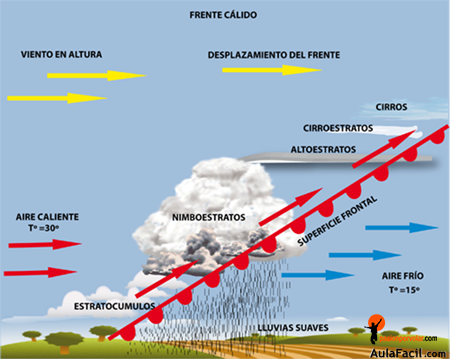
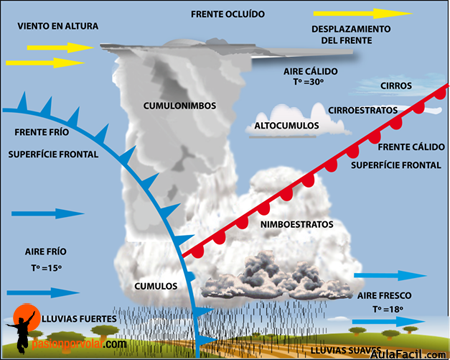
¿Qué es un frente frío?, ¿Qué es un frente cálido?
Un frente frío se forma cuando una masa de aire frio se topa con una masa de aire caliente
La masa de aire frio se mueve más rápido que la de aire caliente, así que la masa de aire frio levanta la de aire caliente para quitarla de su camino.
Al elevarse el aire cálido, su vapor de agua se condensa. Se forman nubes y caen las precipitaciones.
Si el aire cálido es muy húmedo las precipitaciones pueden ser fuertes. Las diferencias entre temperatura y presión de estas dos masas de aire causan vientos que pueden ser muy fuertes en los frentes fríos.
Cuando una masa de aire caliente se topa con una masa de aire frio crea un frente cálido
El aire cálido se mueve más rápido que el aire frio y fluye por sobre la masa de aire frio. Al ascender este aire caliente, se enfría y eso trae nubes y a veces precipitaciones ligeras.
Los frentes cálidos se mueven más lento y cubren un área más amplia. Después de que pasa un frente cálido, la masa de aire caliente tras el trae temperaturas más cálidas, el aire cálido también tiende a ser más húmedo.
En un frente ocluido , una masa de aire caliente se ve atrapada entre dos masas de aire frio. El aire caliente se eleva por sobre el aire frio ( Imagen siguiente ). El tiempo nublado y las precipitaciones a lo largo del frente son comunes.
Ejemplo predicción tiempo rtve:
Probemos a analizar algunos mapas:
¿De dónde vienen los vientos en españa?
Vídeo explica mapas
Climate change:
-rising average temperatures
-extreme weather events
-shifting wildlife populations and habitats-
- rising seas, and a range of other impacts.
The term global warming is just one of the outcomes of climate change. It usually refers to the Earth’s rising surface temperature.
Diferencia entre contaminación del aire y cambio climático
Video about Climate Change and "Think globally act locally"
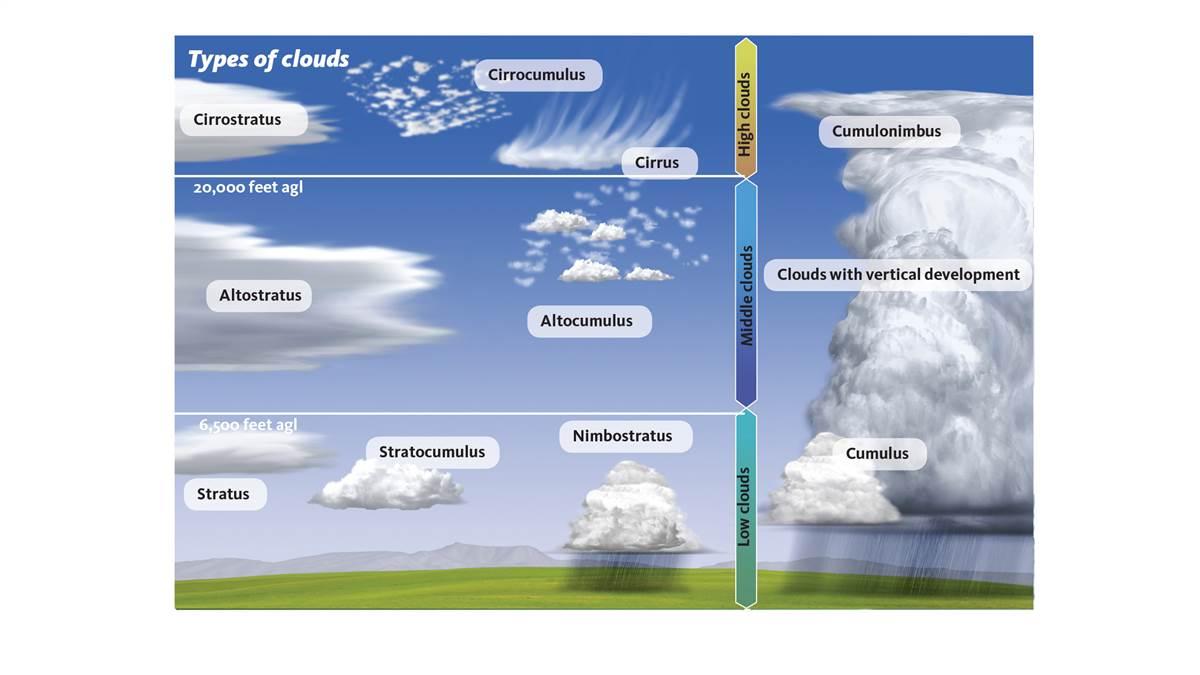
TYPES OF CLOUDS
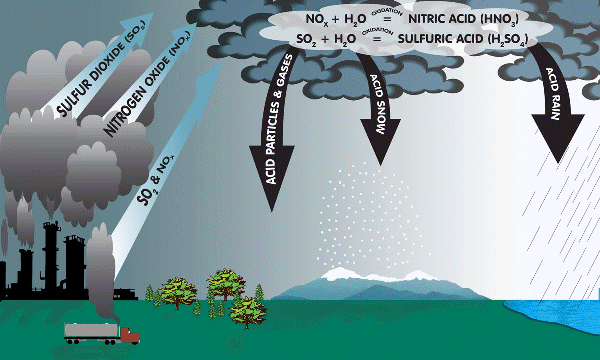
Video about Acid Rain
Ozone hole watch
CFCs destroying ozone
Noticias sobre contaminación atmosférica
- Genially-review activities
THE HYDROSPHERE
What are we going to study in this unit?
UNIT 8- THE BIOSPHERE
LIBRO DIGITAL EN ESPAÑOL
Libro anaya en ingles
Video Let´s explore the characteristics of life. Motivational video
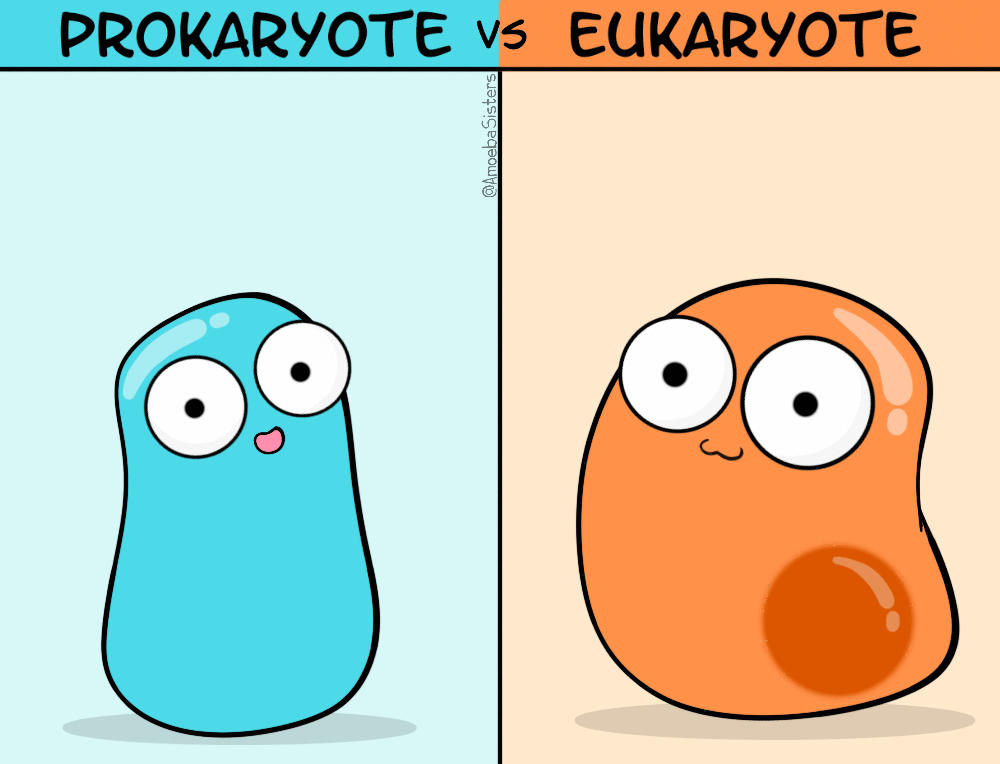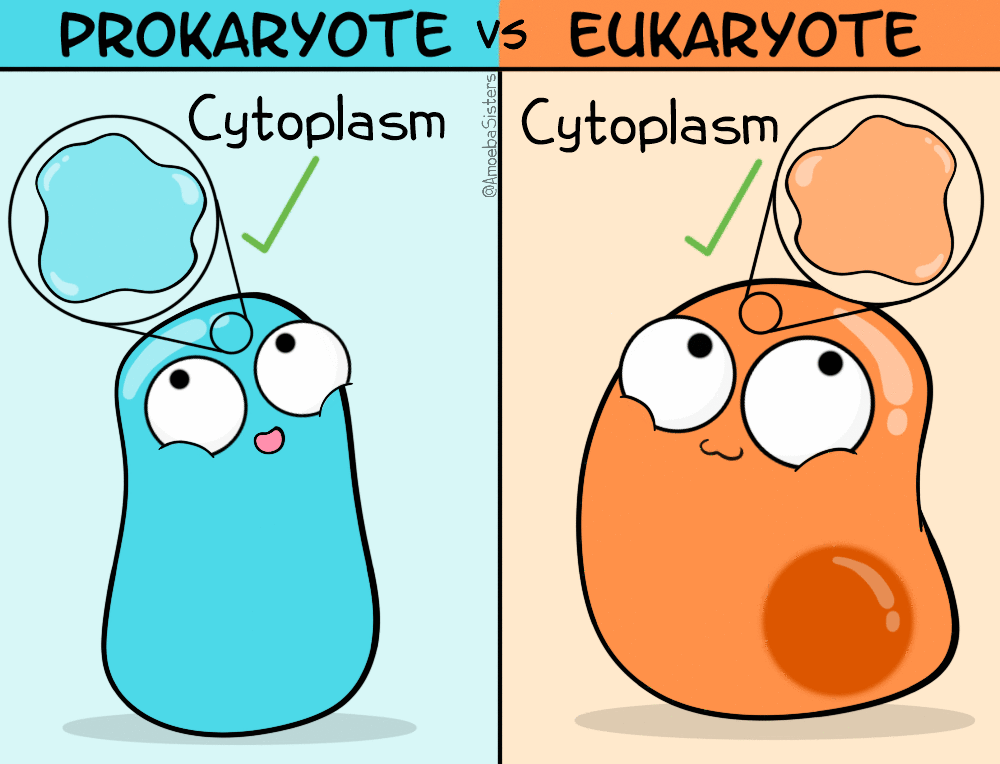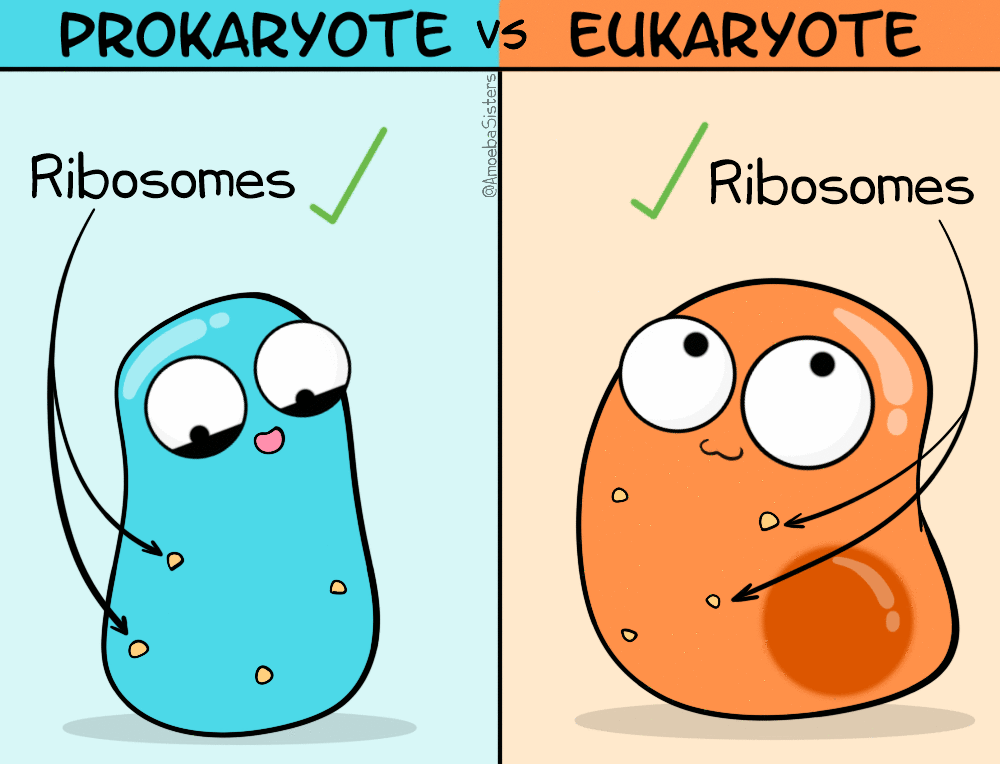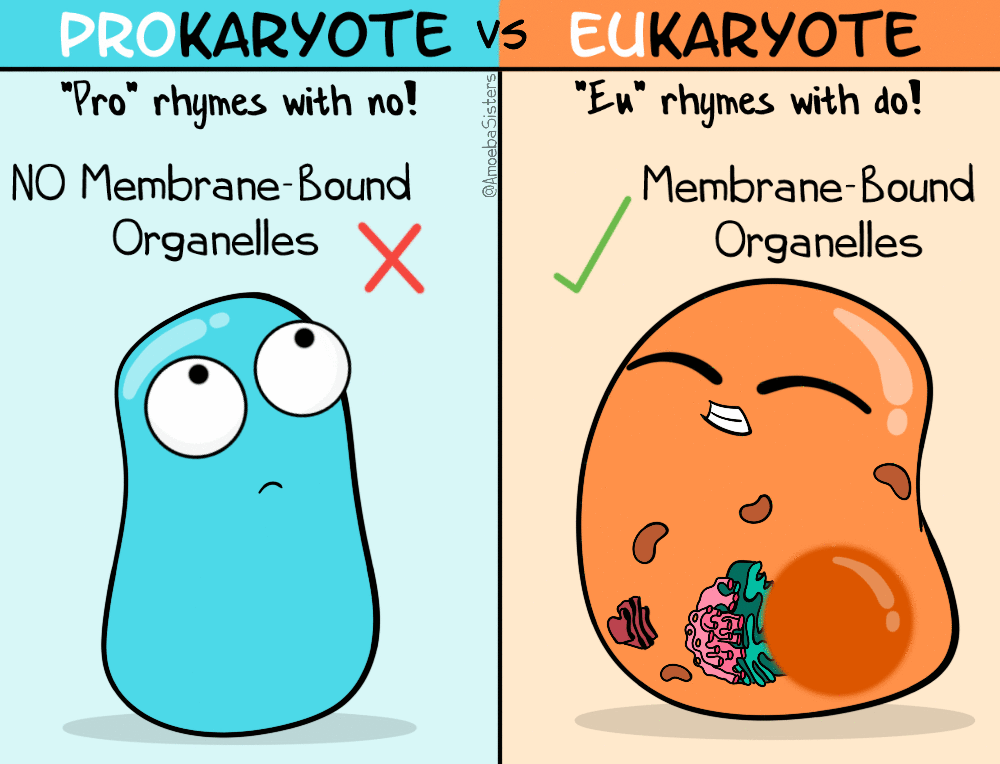
TYPE OF CELLS
3D animation prokaryotic cell
3D animation eukaryotic plant cell
Another animation of cells 3D
Review concepts:
What are cells?
What types are there?
What do all cells have in common?
What are the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Animation to review the main parts of a eukaryotic cells
Liveworksheet review activity cell parts
Pdf to review name of main eukaryotic animal cell parts
Eukaryotic plant cell parts review pdf
Vídeo la célula eucariota animal y vegetal, partes
Reviewing concepts
Enlace a partes célula procariota
Repaso partes célula eucariota
The inside part of a cell is called______, chemical reactions happen here.
What controls everything?
What organelle contains chlorophyll?
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
Video crecimiento células hasta formar renacuajo. Espectacular
Activity levels of organization
REVIEW ACTIVITIES
Actividad repaso partes células animal y vegetal
Actividad-Juego sobre la célula de ampliación en español
True or false?
1- Bacteria have tissues.
2- Animals have tissues.
3- Prokaryotic cells have a nucleus.
4- Eukaryotic plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts.
5- Eukaryotic animal cells have DNA inside the nucleus.
6- Living and non-living things are made of cells.
Draw a eukaryotic animal cell, label the name oif the main organelles
Make up a scientific name
Write the name of the 5 kingdoms and two things about each
THE CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
Actividad clasifica seres vivos
Activity to review the taxonomic category
Explicar como evolucionó la clasificación de los seres vivos con ele jemplo del señor de los anillos
Page and Video explains the binomial nomenclature and the taxonomic categories
Let´s try to match these plants with their scientific names (pdf one drive)
Ideas sencillas sobre los 5 reinos en español
Activity to review kingdoms
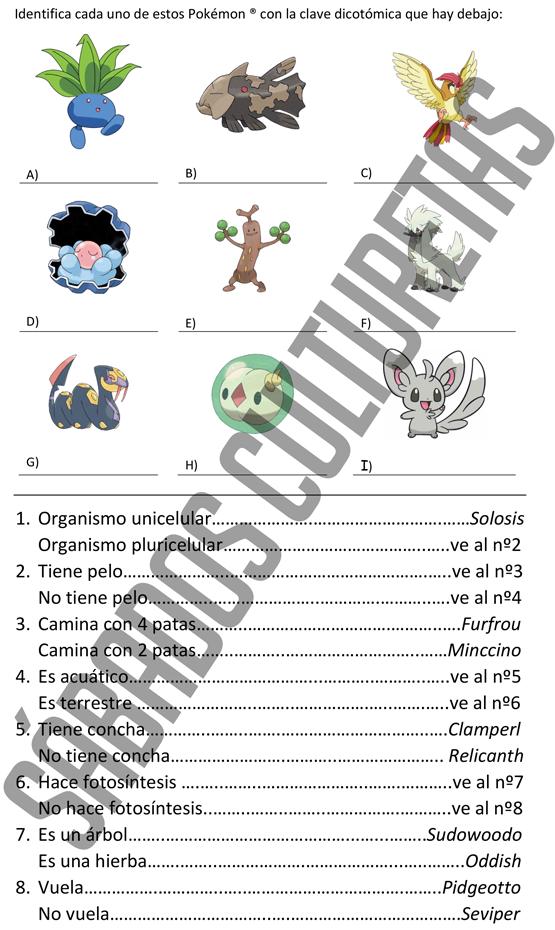
Clave dicotómica para practicar
THE PROJECT FOR THIS UNIT: MAKE A CELL MODEL
Make your cell model (prokaryotic or eukaryotic, animal or plant). I will give you the items that will be evaluated. There are different options:
- You can use food to make a pizza, then you can eat it. I show some pictures to give you ideas:



- You can use other materials or use recycled materials to make your cell modell

Enlace a explicación partes microscopio
Vídeo partes microscopio
Link a un microscopio virtual
Foldscope, el microscopio de origami
Biomaratón
Link to videos, animations about cells
ANIMAL KINGDOM
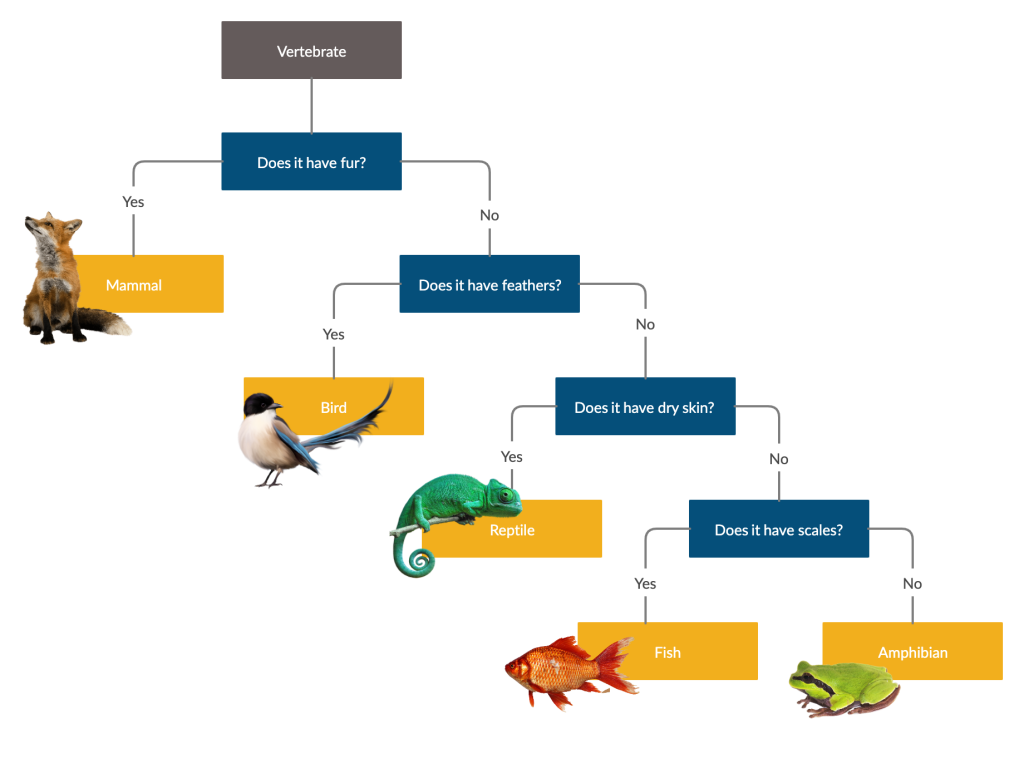
VERTEBRATES
Online activities
ANIMAL BODY PARTS
Vídeo qué animal Islas Medas
Minuto 2:48 Mero / 5 Caballitos de mar/6:22 tiburones
Vídeo qué animal Mallorca
Vídeo metamorfosis rana
Easy exercise about frog´s metamorphosis
Vídeos tortugas
Vídeo cocodrilos
Vídeo sobre el cuco
Vídeo martín pescador
Vídeo pájaro carpintero
Vídeo nacimiento canguro gris
Vídeo oso panda
Vídeo equidnas, ornitorrinco
Vídeo suricatos
Enlace a observaciones con el microscopio
Observación de estomas de una hoja
ANIMAL KINGDOM: INVERTEBRATES
Video crab moulting
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xdikIwIjnWIhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F8JaAWIPnX0 Video metamorfosis mariposa
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ocWgSgMGxOchttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G3VMl-EY2DM
Vídeo interior de un termitero
Avispa común- avispa asiática
Vídeo sobre la avispa asiática
Articulo sobre la 'alarma' de las abejas para evitar ataques de avispas gigantes
CRUSTÁCEOS
Vídeo muda caparazón crustáceos. centollo
Vídeo sobre los cangrejos de río en España
Noticia sobre plaga cigarrras EEUU 2021
Los entomólogos creen que las cigarras periódicas evolucionaron para emerger de cada 13 a 17 años para evitar sincronizarse con el auge de población de sus depredadores.
La previsibilidad de su ciclo hace posible que los agricultores planifiquen con antelación, dijo.
Las cigarras, que se alimentan de la savia de los árboles y las plantas, cuentan los ciclos de helada y deshielo en un “sistema de recuento interno” que les indica cuándo es el momento de salir a la superficie
Los sonidos de hasta 90 decibelios pueden registrarse directamente debajo de un árbol lleno de cigarras. Una motocicleta, en comparación, puede emitir sonidos de hasta 95 decibelios, que pueden dañar el oído tras unos 50 minutos de exposición continua
Video review the main characteristics of invertebrates
Online test about invertebrates
Test about arthropods
ARTHROPOD POETRY
millipede arthropods insect larva
molting metamorphosis
crustaceans antennae
1. When I'm scurrying, fast and fleet,I seem to have a thousand feet.
When I slow down, it's evident
I have just four on each segment.
Who am I? ____________
2. My exoskeleton never grows
Even though I do
And so I have to take it off
To grow one bigger and new.
What is this process? _____________
3. When I come out of an egg
I look like a worm with legs.
But someday - wait and see -
An adult insect I'll be.
What am I? _____________
4. We're crustaceans, arachnids, and millipedes
We're also insects and centipedes.
We're famous for our legs that are jointed
Guess who we are, or we'll be disappointed.
Who are we? ____________
5. My body has three main parts,
An abdomen, thorax, and head
I often fly to get around
Or I use my six legs instead.
Who am I? ____________
6. Lobsters, crabs, and crayfish are we,
We often make our homes in the sea.
We have five pairs of legs to walk
And eyes often perched atop a stalk.
Who are we? _____________
7. We're long and thin.
We're used so much.
When arthropods taste, hear or touch.
What are we? ___________
8. First egg, then larva, then pupa --
Everything gets rearranged,
As step by step I become an adult
And my body's completely changed.
What is this process? ___________
Vídeo bastante técnico sobre evolución y cnidarios
https://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/ed490f06-d5c5-4816-bfc2-75beb2f54011/worlds-most-awesome-invertebrate/
Life cycle of a butterfly
https://wordwall.net/es/resource/5210401/metamorphosis-butterfly-life-cycle
Tracheal respiration (insectos y artrópodos terrestres)
DISECCIÓN DE MEJILLÓN Y CALAMAR. PARTES
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ssgx5MKGFD0
.jpg)
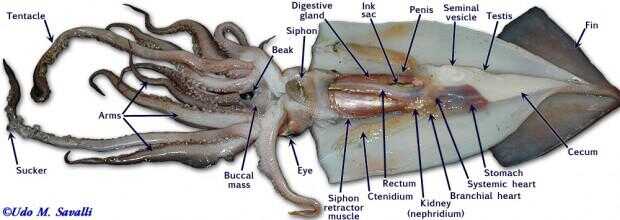
PLANTS- ASEXUAL AND SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Ver partes antera polen
Video pollination
Video the importance of pollinators in crops
Video importancia de la diversidad de abejas
Video What is a herbarium?
Video nutrient cycling
Vídeo colibrí y su polinización
Noticia sobre polinización a mano en China
ECOLOGY: ECOSYSTEMS
Concepto de cascadas tróficas
Cómo los lobos cambiaron el curso de un río (en inglés con subtítulos)
Vídeo en español
Relación entre la malaria y las ranas
Las poblaciones de anfibios empezaron a declinar en la región a partir de principios de los 80, debido a la incidencia de una quitridiomicosis provocada por un hongo . La micosis ha tenido efectos devastadores sobre las poblaciones de anfibios en todo el mundo y a ella se atribuye la desaparición de 90 especies y la reducción de los efectivos de varios centenares más.
El equipo de investigación observó que la incidencia de la malaria en los cantones (Costa Rica) y distritos (Panamá) estudiados se elevó, tras la pérdida de los anfibios, durante tres años.
Recapitulemos: el hongo patógeno mata a los anfibios. Menos anfibios comen menos mosquitos, por lo que estos abundan. Los mosquitos hembra, que ahora son más numerosos y se alimentan de sangre, pican a más personas y les transmiten el protozoo, de manera que son más los que enferman de malaria.
Conviene recordar que la expansión de micosis como la que afecta a los anfibios está provocada, en muchos casos, por actividades humanas, como el tráfico ilegal de animales vivos, o es facilitada por el tráfico internacional de mercancías.
Esto no hace sino reforzar la noción de que para garantizar la salud humana es necesario también cuidar la de los ecosistemas y la de sus integrantes. Es la noción “One health”
¿Si cazamos jabalíes su número aumentará o dismunirá a medio plazo?
El viaje no tan circular de lo residuos domésticos
Vídeo Jane Goodall





































.jpg)




























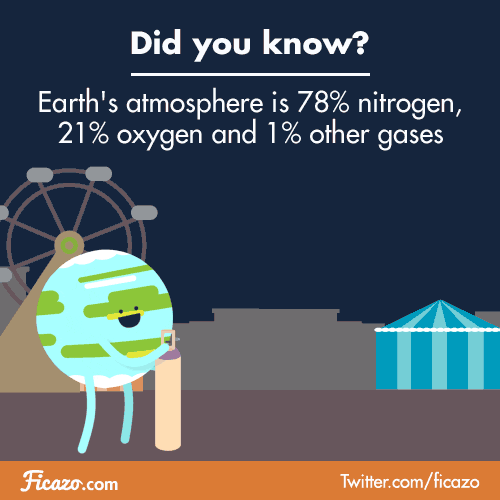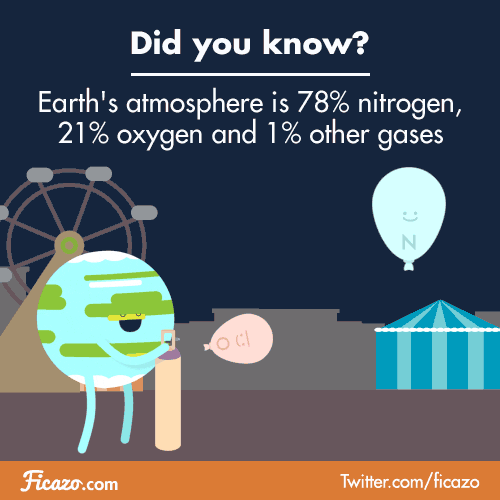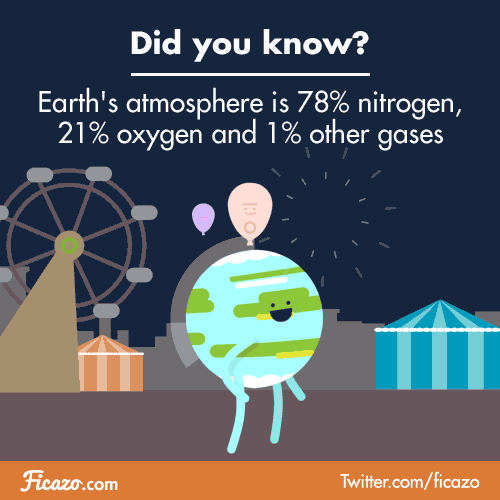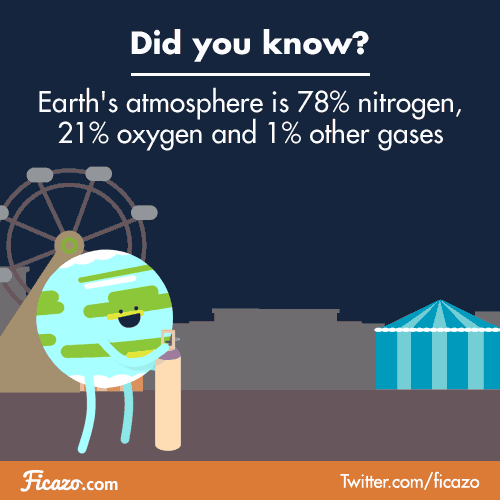























































.jpg)





.jpg)





















No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario